What is Contact Dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis (contact dermatitis) is a health problem characterized by skin rash and itching that occurs as a result of direct contact with an irritant or allergenic substance. For this reason, it is possible to answer questions such as “What is contact dermatitis, what does contact dermatitis mean?” as a skin disease that develops as a result of contact (contact) with allergic or irritant substances. Contact dermatitis, a common inflammatory skin disease, is divided into two classes: allergic contact dermatitis and irritant contact dermatitis, depending on the substance causing the inflammatory response. Contact dermatitis usually resolves spontaneously within a few weeks or days after contact with the allergen or irritant is stopped. However, in cases where symptoms are severe, specialists can use medicines or creams to help relieve symptoms.
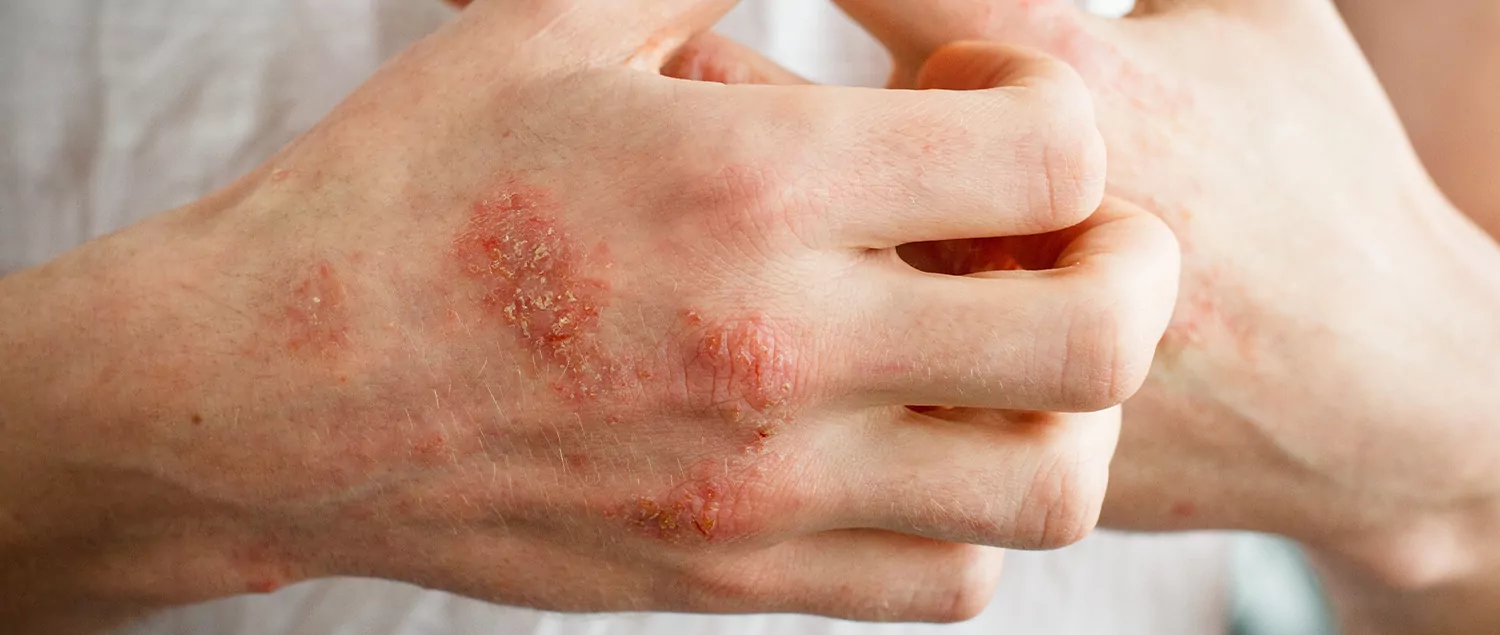
What are the Types of Contact Dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis is a common skin condition reported to affect 5-9% of men and 13-15% of women. Contact dermatitis is more common in people working in various occupational groups, especially in the manufacturing industry. Research shows that occupational skin diseases account for about 30% of occupational diseases, and contact dermatitis accounts for about 90% of occupational skin diseases. Contact dermatitis is an inflammatory skin disease (a type of immune response) that occurs as a result of a reaction of the skin to substances with which it comes into contact. This skin disease is divided into two main classes: irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis. Irritant contact dermatitis is a reaction caused by substances that directly damage the skin when they come into contact with it, such as chemicals or cleaning agents. Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when the skin develops hypersensitivity to certain substances.
What is Allergic Contact Dermatitis?
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a type of eczema that occurs when the immune system overreacts to a substance that comes into contact with the skin. In other words, for those who wonder “What is allergic contact dermatitis?”, AKD can be briefly answered as an allergic reaction that develops in the contact area of the skin against allergens. Allergic contact dermatitis can develop as a nickel allergy or allergy to cosmetics such as perfumes and deodorants. When the skin comes into contact with the substance, the immune system may recognize it as foreign and become defensive. If the skin has been in contact with the substance before, i.e. if the person is sensitized to it, the immune system may develop a more severe reaction on the next contact. As a result, symptoms such as skin redness, itching, blisters, and exfoliation may occur. According to various studies conducted in recent years, allergic dermatitis is a common skin condition affecting about 20% of the population.
What is Irritant Contact Dermatitis?
Irritant contact dermatitis is an inflammatory skin disease that develops as a result of exposure to irritating chemicals such as detergents. Irritants can cause damage to the skin barrier when they come into contact with the skin. It is more common than allergic contact dermatitis. Irritant contact dermatitis may be more common in certain occupational groups such as healthcare workers, catering workers, metal workers, hairdressers and construction workers. Irritant contact dermatitis usually appears within a few minutes after exposure to the irritant, while allergic contact dermatitis can take several days to appear.
What Causes Contact Dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin is exposed to an allergen or irritant. The main allergens that cause contact dermatitis can be listed as follows:
- Metals such as nickel used in the manufacture of various items, especially jewelry,
- Formaldehyde used in various sectors, especially in the textile industry or in the production of paints and plastic materials,
- Personal care products such as deodorants, perfume, shower gel,
- Plants such as poison ivy and mangoes that contain an allergenic substance called urushiol,
- Airborne contact with allergens such as dust, insect spray, pollen,
- Some sunscreens.
In addition to the allergenic substances listed above, in some cases allergenic substances that enter the body through food or otherwise can also trigger allergic dermatitis. There are many irritants that cause contact dermatitis. The main causes of irritant contact dermatitis are as follows:
- Cleaning products such as bleach, dishwashing detergent,
- Body fluids such as urine and saliva,
- Acids
- Herbs like pepper, nettles,
- Cosmetic products such as hair dye and acetone,
- Paints and varnishes,
- Personal care products such as soap and shampoo,
- Materials such as resin, plastic or epoxy,
- Substances in the air, such as sawdust.
The allergens and irritants listed above can affect different parts of the skin. For example, in men who are sensitive to detergents used for washing clothes, contact dermatitis can affect the penis and surrounding area. Likewise, women may experience symptoms such as redness and itching in the genital area.
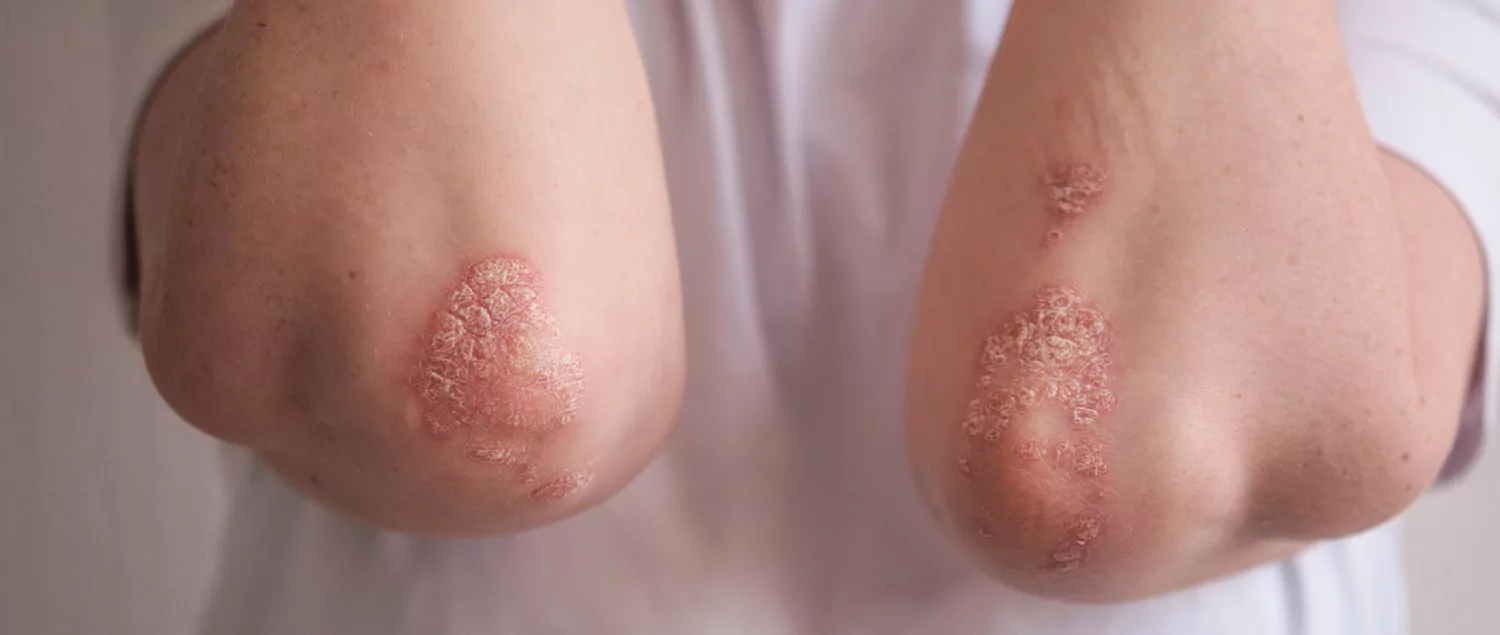
What are the Symptoms of Contact Dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis can manifest itself on the skin with symptoms such as redness, itching, burning sensation and flaking in the affected area. For example, cosmetics such as some sunscreens can cause contact dermatitis on the face, while shampoos can cause dermatitis on the scalp. Contact dermatitis can also affect the eye area, lips, hands, arms and fingers, feet and legs. The main symptoms of contact dermatitis are as follows:
- Darker than normal (hyperpigmented) spots, especially in people with dark skin color,
- Redness
- Itching
- Dryness, cracking and flaking of the skin, especially in fair-skinned people,
- Blisters resembling pimples (may be filled with fluid and crusting may occur),
- Burning and stinging sensation,
- Pain in some cases.
Symptoms of contact dermatitis may not always appear at an early stage. In other words, it also varies according to the duration of exposure to the allergen or irritant. For example, symptoms of occupational contact dermatitis can often occur as a result of prolonged and repeated exposure.
How to Treat Contact Dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis can usually be easily diagnosed by physical examination by specialized dermatologists. In addition, diagnostic methods such as the patch test, which is currently used in the diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis, can be used to identify the allergen to which the person is sensitive. For this reason, during the treatment of allergic contact dermatitis, specialists first advise the patient to avoid the substance to which they are thought to be allergic. There are also some creams and medications that are used to treat both allergic and irritant contact dermatitis. These medicines can help relieve a person’s symptoms and calm the skin. Irritant dermatitis usually has a faster healing process, while allergic dermatitis can take 2-4 weeks to heal. In other words, the healing process of contact dermatitis may vary depending on the type of the disease.
What is Good for Contact Dermatitis?
In most cases, contact dermatitis resolves spontaneously with the cessation of exposure to the substance causing eczema. However, contact dermatitis can also affect babies and children and cause restlessness. Especially babies’ skin is more sensitive than that of adults, which can make them more vulnerable to allergens and irritants. Therefore, the answer to the question “How does contact dermatitis go away?” is important for parents. Some home remedies can help alleviate contact dermatitis. The main methods are as follows:
- Avoiding allergens or irritants,
- Regular use of creams recommended by doctors to help relieve itching and soothe the skin,
- Applying cold compresses for 15-30 minutes at regular intervals,
- Cutting nails or putting gloves on babies as nails can increase skin irritation,
- Gently drying hands after washing them.
In addition to the above, the use of moisturizing products can also help alleviate symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Contact Dermatitis Spread?
Since the symptoms of contact dermatitis are similar to those of sexually transmitted diseases such as herpes (genital herpes), it may be considered contagious. However, contact dermatitis is not a contagious skin disease.
What Should Contact Dermatitis Not Eat?
Since contact dermatitis is often caused by contact with an allergen or irritant, there are no strict restrictions on dietary habits. However, in some cases, vegetables such as onions and garlic can trigger symptoms of dermatitis. Therefore, it may be useful to identify the factor causing contact dermatitis in the individual and prepare a personalized nutrition plan
When Does Allergic Contact Dermatitis Go Away?
Allergic contact dermatitis may resolve within 2-4 weeks after stopping exposure to the allergen.
Does Contact Dermatitis Go Away on Its Own?
Contact dermatitis can resolve spontaneously by avoiding contact with allergens or irritants.
However, it is important to seek help from a specialist doctor as contact dermatitis can in some cases cause serious complications such as anaphylactic shock (a severe allergic reaction that affects different tissues and organs of the body, including the respiratory tract).




